Single CPU Server vs Dual CPU Server: What’s The Choice
In our rapidly evolving tech world, the quest for robust and efficient server configurations is on the rise. Central to this quest is the decision regarding the number of central processing units (CPUs) – the server’s heartbeat. Opting for a single or dual central processing unit server can greatly affect performance, scalability, and cost.
This piece delves into the “Single vs. Dual processor server” discussion, highlighting the factors that sway the decision. We’ll discuss the pros and cons of both setups, juxtapose their performance, and evaluate their fit for different workloads.
We’ll touch upon performance metrics, scalability potential, upgrade paths, and the financial implications of each setup. With this insight, you’ll be better equipped to make a choice that aligns with your application’s needs, scalability goals, and budget.
If you’re contemplating purchasing an unmetered dedicated server, journey with us through the realms of single and dual-core servers, understanding their merits, demerits, and the optimal pick for your hosting prerequisites.
Also Read: Best Alternatives to OrcPub
Grasping CPU Servers
To make a well-informed choice between single and dual-core servers, it’s pivotal to grasp the essence of processors in computing.
Processing servers, the pillars of computing infrastructure, are tasked with instruction execution, data processing, and system operation management. Often dubbed the server’s “mind”, the processor performs calculations, oversees data movement, and synchronizes tasks among various elements.
Core Distinction: Single vs. Dual CPU Server
A single server with central processing units boasts one processor, whereas its dual counterpart has two. Processors, or CPUs, have multiple cores capable of performing multiple tasks at once. Independent core operation allows for parallel processing and improves performance.
DID YOU KNOW?
A Core is a physical part of a CPU. Cores act like processors within a single CPU chip. The more cores a CPU has, the more tasks it can perform simultaneously.
The single vs. dual processor server choice hinges on intended use, workload demands, and budgetary limits. Single processing unit servers are apt for smaller applications or lighter workloads, offering cost efficiency, energy conservation, and straightforward management. Conversely, dual processing unit servers cater to heavy-duty tasks, large enterprise applications, and situations demanding high computational power and simultaneous workloads.
To pinpoint the ideal configuration, one must understand the strengths and weaknesses of both setups. In the subsequent sections, we’ll delve into the performance, scalability, and cost aspects of both configurations.
Computational Might: Single vs. Dual CPU Server
The central processor count directly influences a server’s computational prowess. A single processing unit (CPU) server, with its lone processor, might falter in front of a dual-core server when handling intricate computations or resource-heavy applications, potentially slowing down operations.
Conversely, a dual CPU server, with its doubled computational strength from two processors, shines in managing hefty workloads and parallel processing. It can multitask efficiently, promising enhanced performance and swift responses.
Multitasking Proficiency: Dual vs. Single CPU Servers
The number of cores per processor is important when assessing a system’s ability to multitask. Even though single servers can manage moderately simultaneous operations, they might stumble when juggling multiple intensive tasks, leading to potential slowdowns.
Dual systems, with their dual processors, distribute tasks efficiently, ensuring seamless operations even under heavy workloads.
In essence, whereas single-core servers manage moderate workloads, dual-core servers, with their paired processors, reign supreme in parallel processing, making them the go-to for scenarios demanding simultaneous execution of intensive tasks.
Cost Dynamics: Single vs. Dual CPU Servers
Cost considerations are multifaceted. Single servers are typically more wallet-friendly, both in terms of initial investment and operational costs. However, for those requiring amplified processing power and the ability to perform multiple tasks, the steeper investment in a dual server might be justifiable.
Scalability Spectrum: Dual vs. Single CPU Servers
Single CPU servers cater well to lighter workloads, such as personal sites or basic applications. They’re cost-effective, energy-efficient, and user-friendly. Dual CPU servers, on the other hand, are tailored for demanding tasks, making them apt for intricate computations, data-heavy processes, and multitasking-intensive scenarios.
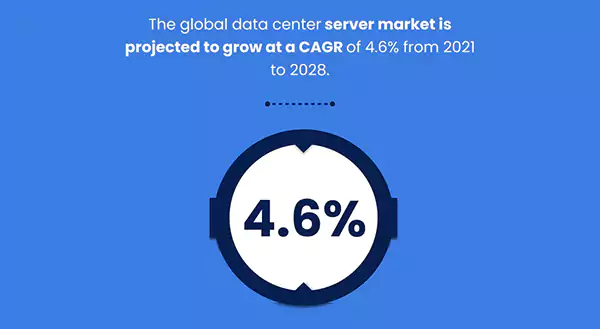
The global data center server market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.6% from 2021 to 2028.
Workload Compatibility: Single vs. Dual CPU Servers
The server choice should resonate with your application’s workload demands. Single servers are apt for simpler workloads, whereas dual servers are tailored for demanding tasks, ensuring smooth operations and swift task execution.
Resource Management: Single vs. Dual CPU Servers
In single-core servers, the lone processor manages all resources, which can lead to potential bottlenecks in high-demand situations. Dual processor servers, with their dual processors, ensure optimal resource distribution, leading to enhanced performance, especially in situations involving multiple tasks.
Comparing Single and Dual CPU Servers: Which is Right for You?
A Single processor Server is tailored for tasks that don’t demand hefty processing capabilities. It’s perfect for hosting personal sites, running small-scale business apps, managing light databases, and operating standard office software.
These servers are typically more budget-friendly, energy-efficient, and straightforward to oversee, making them a go-to for less demanding tasks.
On the flip side, Dual Servers shine when there’s a need for robust processing capabilities. They’re designed for intricate calculations, handling data-rich operations, supporting virtualization, excelling in high-performance computing, and situations that call for simultaneous tasks.
With a Dual Server, running several apps at once becomes a breeze, ensuring seamless operations and quicker processing of heavy-duty tasks.
When torn between a Single and Dual Server, weigh in on your workload’s specific demands. For tasks that are on the lighter side and don’t need much processing muscle, a Single-core Server should do the trick.
But if you’re dealing with high-demand applications or multitasking environments, a Dual Server might be your best bet.
Deciding Between Single and Dual CPU Servers Based on Workload
The key to optimal server performance lies in aligning your server choice with your application’s workload needs. When juxtaposing the efficacy of a Dual core Server with a Single core Server, it’s vital to gauge their individual merits and potential.
A Single processor Server is a match for tasks that aren’t too processing-intensive. It’s adept at running personal sites, supporting small enterprise apps, overseeing light databases, and basic office tools.
Given their cost benefits, energy conservation, and ease of management, they’re a sensible pick for tasks with modest resource needs.
Conversely, Dual-core Servers are powerhouses for tasks that are resource-hungry and require substantial processing might. They’re cut out for intricate mathematical tasks, data-heavy operations, virtual setups, top-tier computing, and a variety of scenarios. With these servers, you can effortlessly juggle multiple apps, ensuring fluid operations and swift task execution.
In the Single vs. Dual-core Server debate, it’s imperative to dissect your workload’s unique needs. Ponder over aspects like your application’s nature, the number of simultaneous users, computational intricacies, and multitasking necessities.
Such introspection will steer you towards choosing either a Single or Dual core Server that aligns with your workload’s demands.
Resource Management: Single-Core vs Dual-Core Servers
In a Single-Core Server setup, the entire system’s resources are channeled through one processor. This implies that the CPU is responsible for managing all tasks and distributing resources as needed.
Such a setup can efficiently handle basic workloads, but during peak demand, it might face resource clashes and potential slowdowns. The lone processor’s resource management becomes a pivotal factor in determining performance.
Conversely, Dual-Core Servers bring a more balanced resource distribution to the table. With a pair of independent processors, tasks can be evenly spread out, leading to optimal resource use and a boost in system performance.
Each processor can focus on distinct tasks, enhancing multitasking and reducing resource clashes. This ensures a fluid operation and heightened responsiveness, especially when dealing with multiple simultaneous processes or running heavy-duty applications.
When weighing the options of a Single-Core Server against a Dual-Core Server, it’s vital to gauge the resource needs of your tasks and select the setup that can most efficiently cater to those needs.
System Resilience: Single-Core vs Dual-Core Servers
With a Single-Core Server, the processor stands as the sole point of vulnerability. Should the CPU encounter an issue, the entire system grinds to a halt until the processor is either fixed or replaced. Such a weak point can lead to extended periods of inactivity, potentially hampering business functions.
On the flip side, Dual-Core Servers come with an inherent backup system. Should one core face issues, its counterpart can take over the workload, ensuring minimal interruptions and heightened system resilience.
The backup CPU acts as a safety net, allowing the server to function even if one processor encounters problems. This built-in redundancy significantly boosts server dependability and lessens the repercussions of hardware malfunctions.
Given their resilience, Dual-Core Servers are ideal for complex applications and settings that prioritize constant availability. By reducing downtime risks and offering efficient backup mechanisms, Dual-Core Servers guarantee consistent functionality and data safety.
Server Virtualization: Single-Core vs Dual-Core Systems
Virtualization technology has surged in popularity as a means to enhance server productivity and optimize resource allocation. Here’s a breakdown of the virtualization prowess of Single-Core Servers in comparison to Dual-Core Systems.
Single-core servers offer virtualization capabilities, up to a point. They can accommodate a finite set of virtual machines (VMs) based on the available processing strength and resources.
Yet, the lone processor might become a bottleneck when tasked with operating several VMs at once or managing demanding virtualized tasks. This could lead to a dip in performance and flexibility in virtual settings.
On the other hand, Dual-Core Systems shine in virtualization contexts. With two autonomous processors at their disposal, these servers can more evenly allocate resources across VMs, leading to heightened performance and agility.
Dual-core systems can oversee a broader array of VMs and are adept at managing more demanding tasks, positioning them as the go-to choice for virtual settings that necessitate extensive consolidation and adaptability.
Level Up Your Online Presence: How iTop Screen…
Vidnoz AI Review: How to Convert Text to…
HitPaw Online Video Enhancer Review and Its Best…
Top 7 Background Removers Online in 2024
How to Retrieve Google Backup Photos?
How Does The Image-To-Text Tool Work?
SwifDoo PDF Review 2024: A Comprehensive Look
The Real Benefits of DevOps Training for Aspiring…
Capturing Serenity: Elevating Yoga Pose Photos with CapCut’s…
Boost Your Productivity with a Desktop-Docked Search Utility…
Windows Server Backup Software: Securing Your Critical Data…